Unifying Blockchain Ecosystems with Socket Protocol
The blockchain space has seen the emergence of numerous chains, layers, cross-chain messaging, and bridges. These innovations have significantly increased the functionality and capabilities of the blockchain, enabling a more dynamic and versatile ecosystem. However, fragmentation remains a major challenge with users, liquidity, and states distributed across multiple chains and layers, leading to inefficiencies and complexities. Users find it difficult to navigate different ecosystems, while liquidity is often scattered, reducing the overall effectiveness of DApps.
To address these challenges, Socket Protocol developed an abstraction protocol to unify the fragmented blockchain landscape by providing a seamless and efficient solution. It enables interoperability and connectivity across different chains and layers, ensuring a cohesive and user-friendly experience. By integrating various ecosystems, Socket Protocol simplifies interactions and optimizes liquidity.
What is Socket Protocol?

Source: Socket Protocol website
Socket Protocol is the first chain-abstraction protocol, designed to enable developers to build applications that seamlessly interact across over 300 blockchain networks through chain abstraction. Instead of treating each chain as an independent system, Socket Protocol allows developers to utilize chains as unified infrastructure—much like traditional applications use databases and servers. This provides a standardized way for different blockchain networks to communicate and exchange assets without requiring direct integration with each network’s technical specifics. By abstracting these complexities, developers can build applications that function smoothly across multiple blockchains, eliminating the need to handle each network’s unique implementation.
Vision and Mission

Co-founded by Rishabh Khurana and Vaibhav Chellani, Socket Protocol aims to unify the fragmented blockchain landscape by providing a seamless and efficient solution for interoperability and connectivity. Their mission is to create a cohesive ecosystem where various blockchains communicate and interact effortlessly, enhancing the overall user experience and optimizing liquidity across the blockchain space. Socket Protocol envisions a future where decentralized applications can operate across multiple chains as easily as traditional applications interact with databases.
Key Features of Socket Protocol
- Chain-Abstracted Contracts: Developers can execute contracts across any supported chain using standard Solidity, without dealing with complex messaging protocols or asynchronous handling. This allows for direct function calls with a consistent developer experience.
- Pre-Execution Framework: Developers can run custom logic before onchain execution, enabling advanced features like auctions, intent matching, and security checks. This framework provides full control over the execution flow and user experience.
Products Offered by Socket Protocol
Socket API
The Socket API provides developers with a standardized interface to interact with the chain-abstraction protocol. It abstracts the complexities of multiple blockchain networks, enabling developers to initiate and manage cross-chain transactions using standard Solidity calls. This simplifies application development, as developers do not need to handle each network’s unique implementation details.
Key benefits of the Socket API include:
- Ease of Integration: Developers can quickly integrate the API into their applications without extensive modifications.
- Consistent Developer Experience: The API provides a uniform experience for interacting with different blockchains, reducing developers’ learning curve.
- Enhanced Functionality: The API supports advanced features like automated routing, asset swaps, and cross-chain messaging.
Socket Plugin
The Socket Plugin is a tool that integrates directly with applications built on the Socket Protocol. It simplifies the process of connecting to the protocol, allowing developers to incorporate cross-chain functionality without managing intricate network details. The plugin bridges the gap between application logic and the chain abstraction layer.
Key features of the Socket Plugin include:
- Seamless Integration: The plugin can be easily integrated into existing applications, enabling cross-chain interactions with minimal effort.
- Flexibility: Developers can customize the plugin to meet their specific requirements, ensuring compatibility with various use cases.
- Simplified Development: The plugin abstracts the complexities of cross-chain interactions, allowing developers to focus on core application logic.
SocketScan

SocketScan is a monitoring tool that displays cross-chain activity within the Socket Protocol ecosystem. It provides real-time insights into transaction flows and the performance of chain-abstracted packets across multiple networks. SocketScan serves as a transparent dashboard for users and developers to track and analyze protocol interactions.
Key benefits of SocketScan include:
- Real-Time Monitoring: Users can view live updates on cross-chain transactions and packet statuses.
- Comprehensive Analytics: SocketScan offers detailed analytics and performance metrics, helping developers optimize their applications.
- User-Friendly Interface: The tool features an intuitive interface that makes it easy for users to navigate and understand the data.
Bungee Protocol

Bungee Protocol is a global liquidity marketplace powered by Socket Protocol. It enables users to perform various actions across chains, optimizing for user needs. Users can indicate their desired actions, such as swaps, deposits into DeFi protocols, or minting NFTs, by signing user requests. Bungee Protocol handles the complex parts like onchain execution, routing, and pathfinding through offchain actors.
Key features of Bungee Protocol include:
- Global Liquidity Marketplace: Facilitates cross-chain asset transfers and actions, optimizing for end-user needs.
- Gasless User Requests: Users can dictate their desired actions offchain in a gasless fashion.
- Outsourced Complexity: The protocol handles complex onchain execution, routing, and pathfinding, streamlining the user experience.
- User-Centric Design: Designed to optimize user experience, making cross-chain interactions simple and efficient.
Use Cases of Socket Protocol
Socket Protocol enables powerful applications through chain-abstracted composability and pre-execution capabilities. Here are some key use cases, though this list continues to grow as developers innovate with the protocol:
Horizontal Scaling
Traditional blockchain scaling typically follows two vertical approaches: launching an app-chain or deploying on high-throughput chains. However, these methods create composability challenges, making it difficult for applications and users on other chains or rollups to interact. Socket Protocol enables a different approach called horizontal scaling. Similar to modern web applications, your application can be deployed across multiple chains or rollups simultaneously, with traffic load-balanced between them. Using Socket’s AppGateway, this process becomes seamless for onchain contracts. Several leading applications are already utilizing this approach.
Intent-Based Execution
Socket Protocol allows developers to build sophisticated intent systems that improve user experience and execution efficiency. Through AppGateways, developers can process user intents, run execution auctions, and optimize transaction routing. The protocol’s built-in transmitters enable the immediate implementation of intent-based systems while maintaining full control over security, cost, and performance.
Application-Specific Sequencing
Applications generating Miner Extractable Value (MEV) can benefit from custom transaction sequencing. Rather than letting chain validators capture this value, developers can create AppGateways to sequence transactions, capture and redirect value to designated stakeholders, and implement custom execution ordering. A notable example is Oracle Extractable Value (OEV) capture from swap transactions.
Pre-Execution Security
Unlike traditional security services that operate post-transaction, Socket Protocol enables preventative security through pre-execution checks. Using AppGateways, developers can implement security validations before onchain execution, enforce critical protocol invariants, and proactively prevent potential exploits.
Technology Behind Socket Protocol
Application Gateway

Application Gateways are application-specific top-level functions that can run pre-onchain execution of the application itself. Socket Protocol does not enforce a particular VM or language for these gateway contracts, but assuming EVM for simplicity, developers can leverage the gateway for various use cases. Gateways are hosted offchain by watcher entities, which hold a permissionless role. Applications can select and employ watchers via onchain contracts called switchboards. This setup provides flexibility for selecting multiple watchers and deciding how to validate watcher execution of their gateway contracts. Use cases for gateway contracts include running simulations of all interactions with their onchain applications to increase safety, running auctions to optimize better outcomes for end users, and enabling global routing.
Modular Order Flow Auctions (MOFA)

MOFA is a unique concept leveraged by Socket Protocol to enable developers to create a market for their order flow where third parties compete to fulfill the order flow. It allows application developers to convert an unaligned intermediary into an aligned friend, transforming a potential hurdle into an enabler of chain-abstraction for the application. Applications can now optimize properties they and their users care about, such as price, latency, or other factors. Third parties fulfill user requests onchain as defined by applications, enabling chain-abstraction while delivering value to users and applications.
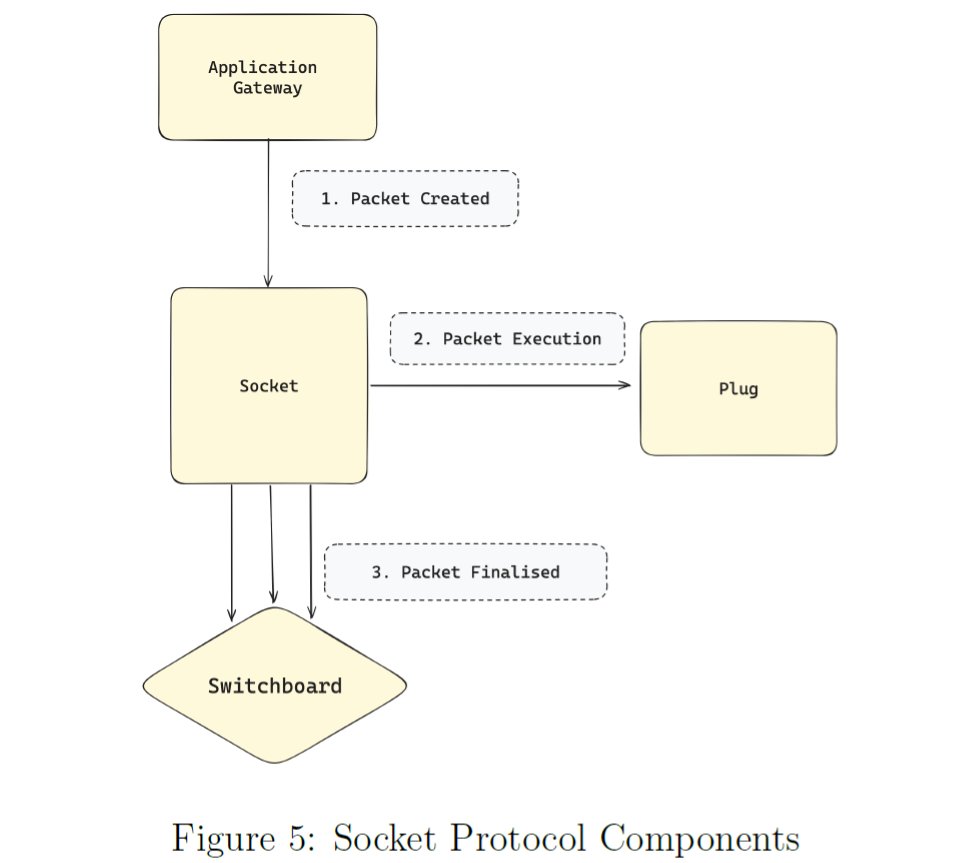
Switchboards

Switchboards are essentially onchain verifier contracts that anyone can write and attach to Socket Protocol. Before executing the application, Socket Protocol checks with the application-selected switchboard, allowing applications to perform various checks before executing their onchain contracts. Think of switchboards as libraries that anyone can use. Examples include a switchboard that allows for plug execution if only a single watcher authorizes execution, a switchboard that employs 100 watchers and allows for execution if 2/3 authorize it, or optimistic, ZK, or oracle-based switchboards that prove the watcher ran the application-defined gateway as intended. Applications will choose different switchboards according to their use case, with varying levels of cost, security, and latency for onchain execution. Applications can switch switchboards as needed.
Watchers

Watchers are entities that run the “watcher service,” reading multiple chains and allowing application developers to deploy gateway contracts on top of the VMs they run. Applications employ watchers via switchboards, making them a crucial part of the system. Key points about watchers include:
- Depending on the switchboard application developers use, they would have varying degrees of trust in this entity.
- Anyone can run a watcher-service and listen to as many or as few chains as they want to participate in the Socket Protocol.
- Participation is subject to applications opting to deploy their gateway contracts on the watcher’s service.
Socket Protocol Architecture
Socket protocol enables developers to build chain-abstracted applications using a combination of offchain agents and onchain contracts. This setup allows for flexible, efficient, and customizable cross-chain interactions.
Watchers
Watchers are offchain operators that monitor blockchain activity and host the Application Gateway (AppGateway). They execute custom offchain logic defined by developers and generate proofs, which are then passed to a Transmitter for onchain verification by a Switchboard. Watchers act as a bridge between the user and the blockchain, enabling developers to insert useful offchain logic before onchain smart contracts are executed. This streamlines processes like high gas fees, complex bridging, and multi-chain interactions.
Key Role of Watchers
- Hosts AppGateways: Specialized VMs run AppGateway contracts, executing custom offchain logic.
- Generate Proofs: Observe blockchain events, execute logic, and generate proofs for onchain verification by Switchboards.
- Passive Role: Anyone can become a Watcher by running a node without special permissions.
How Watchers Fit into the Protocol
- User signs an offchain message and sends it to a Watcher, where AppGateway logic is executed.
- The Watcher generates a proof, which is passed to a Transmitter.
- The Transmitter submits the proof onchain, where it is verified by a Switchboard before triggering the onchain smart contract.
Switchboards
Switchboards are onchain smart contracts that validate offchain proofs generated by Watchers and submitted by Transmitters. They ensure the offchain logic executed in the AppGateway meets the application’s security, cost, and performance requirements.
Key Features of Switchboards
- Permissionless Registration: Anyone can write and register a Switchboard with the SOCKET protocol.
- Lightweight Interface: Designed to be simple and efficient, Switchboards accept proofs from Transmitters and return a boolean (true/false) indicating proof validity.
- Application-Defined: Developers can choose or create Switchboards to meet their security, cost, and latency profiles.
- Proof-Agnostic: Switchboards accept various types of proofs, such as Oracle attestations, zk-proofs, multi-signature proofs, or optimistic submissions.
How Switchboards Fit into the Protocol
- The Transmitter submits a signed user request and proof generated by a Watcher to the onchain SOCKET contract.
- The SOCKET contract forwards the proof to the Switchboard selected by the application developer.
- The Switchboard verifies the proof and returns a boolean (true/false).
- If the proof is accepted, the onchain smart contract is executed.
Transmitters
Transmitters are offchain smart agents responsible for moving user requests and Watcher-generated proofs from offchain to onchain. They coordinate with Watchers to submit data to the onchain SOCKET contract, which then forwards the data to a Switchboard for verification.
Key Role of Transmitters
- Move Data Onchain: Submit proofs generated by Watchers to the onchain SOCKET contract for verification.
- Coordinate with Watchers: Ensure the corresponding proof and user request are submitted to the blockchain for execution.
- Trigger Onchain Contracts: Facilitate the execution of the application’s onchain smart contract once the proof is verified by the Switchboard.
How Transmitters Fit into the Protocol
- The user sends a request to the Watcher, where AppGateway logic is executed, and a proof is generated.
- The Watcher passes the proof to the Transmitter.
- The Transmitter submits the proof and user request to the onchain SOCKET contract.
- The Switchboard verifies the proof and returns a boolean (true/false).
- If accepted, the onchain smart contract is triggered.
Onchain App Contract
Onchain App Contracts are traditional smart contracts deployed on the blockchain that interact directly with the SOCKET ecosystem. These contracts encapsulate decentralized applications’ core logic and functionality (dApps). By integrating with the SOCKET protocol, Onchain App Contracts can leverage cross-chain interoperability and abstract complexity from developers.
Key Roles of Onchain App Contracts
- Execution: They execute predefined functions and business logic based on user interactions and the results of offchain processes.
- Interoperability: They interact seamlessly with multiple blockchain networks, enabling the transfer of assets and data across chains without directly integrating each network’s technical details.
- Security and Decentralization: As deployed onchain, they inherit the security properties and decentralization benefits of the underlying blockchain.
App-Gateway Contract
App-Gateway Contracts are specialized contracts deployed on enhanced virtual machines (EVMx) and serve as intermediaries between users and onchain smart contracts. These contracts handle interactions and enforce specific logic before executing onchain operations.
Key Roles of App-Gateway Contracts
- Pre-Execution Checks: They run custom logic before onchain execution, such as simulations, auctions, intent matching, and security checks.
- Intermediary Layer: They act as a bridge, managing interactions between users and onchain App Contracts, ensuring smooth and efficient communication.
- Enhanced Functionality: They enable advanced features like global routing and composability, improving the overall user experience.
How Socket Protocol Works

Socket Protocol operates by creating and deploying Chain-Abstracted-Packets (CAPs) to enable applications to interact seamlessly across multiple blockchains. This process ensures efficient and secure cross-chain transactions.
- User Request Initiation: A user sends a request to the Application Gateway.
- Gateway Processing: The Gateway, which acts as a connection point for onchain applications hosted by offchain monitoring service operators, receives the user request. The Gateway processes the request and prepares it for the next step.
- Transmitters’ Role: Transmitters, offchain smart actors responsible for moving user requests and proofs from offchain to onchain, receive the processed request. They respond with action proposals on the blockchains.
- Selecting a Suitable Transmitter: The Application Gateway selects the most suitable Transmitter based on specific conditions such as cost, latency, and security.
- Creating Chain-Abstracted-Packets (CAPs): The selected Transmitter generates a CAP, which includes request and response information along with an authentication signature from the Watcher.
- Execution by Transmitters: The Transmitter executes the CAP on the relevant blockchain networks. The application’s smart contract (Plug) performs the required actions.
- Validation by Switchboards: Switchboards, which are onchain smart contracts, validate the CAP to ensure its validity and security. Switchboards allow applications to choose from various monitoring and authentication services such as Optimistic or Zero Knowledge Rollups.
- Completion and Transparency: This process continues across different networks until all actions in the CAP are completed. Components such as Watchers and Transmitters ensure transparency and efficiency in execution, making the Socket Protocol a powerful and flexible solution for multi-chain applications.
Socket Protocol’s Fundraising Journey
Socket Protocol has made significant strides in securing funding to support its mission of enhancing blockchain interoperability. In March 2022, Socket Protocol secured a $5 million seed round. This funding round attracted several key investors, including Coinbase Ventures and Framework Ventures. The investment aimed to expand Socket’s work with Coinbase, providing bridging opportunities for developers and users of Coinbase Wallet and Base.
The most recent fundraising milestone occurred in September 2023, when Socket Protocol raised another $5 million in a strategic round. This round was also led by Coinbase Ventures and Framework Ventures, further solidifying their support for the project. The new capital will enhance the protocol’s capabilities and expand its reach within the blockchain ecosystem.
Conclusion
Socket Protocol addresses fragmentation challenges within the blockchain ecosystem by enabling seamless interactions across multiple blockchain networks. By leveraging chain abstraction, it allows developers to build sophisticated cross-chain applications. Socket Protocol ensures efficient, secure, and scalable cross-chain transactions through innovative technologies like Application Gateways, Modular Order Flow Auctions, Switchboards, and Watchers. Its suite of products, including the Socket API, Socket Plugin, SocketScan, and Bungee Protocol, enhances both developer and user capabilities. Supported by successful fundraising and prominent investors, Socket Protocol is poised to simplify cross-chain interactions and create a truly interconnected ecosystem.
Related Articles

Unleashing the Power of GRIFFAIN Token: Solana Labs' Financial AI Agent

UniversalX – A New Paradigm for Meme Coin Trading Through Chain Abstraction and Cross-Chain Connectivity

Gate Research: A Comprehensive Look at Web3 Cross-Chain Services - Leading Protocols, Innovations, and Challenges

Chain Abstraction and On-Chain Trading Evolution

What is Particle Network (PARTI)?


